Given the root of a binary tree and an integer limit, delete all insufficient nodes in the tree simultaneously, and return the root of the resulting binary tree.
A node is insufficient if every root to leaf path intersecting this node has a sum strictly less than limit.
A leaf is a node with no children.
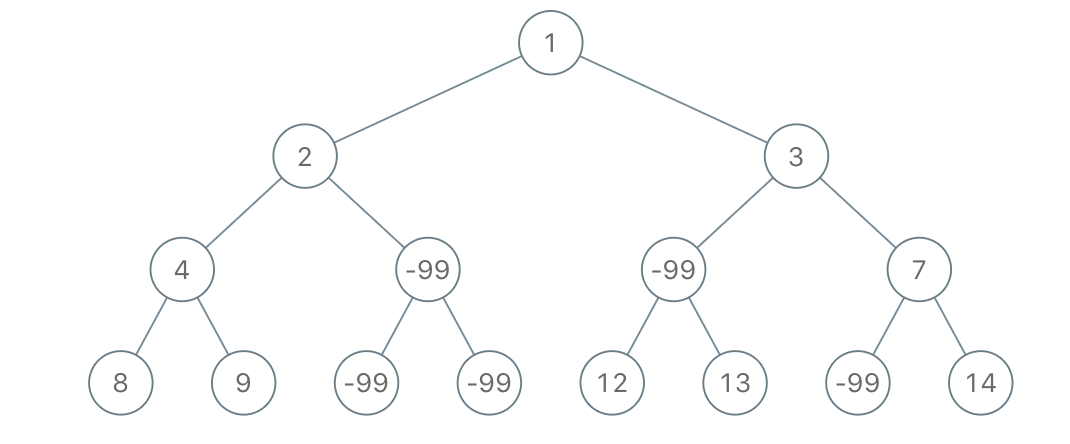
Input: root = [1,2,3,4,-99,-99,7,8,9,-99,-99,12,13,-99,14], limit = 1 Output: [1,2,3,4,null,null,7,8,9,null,14]
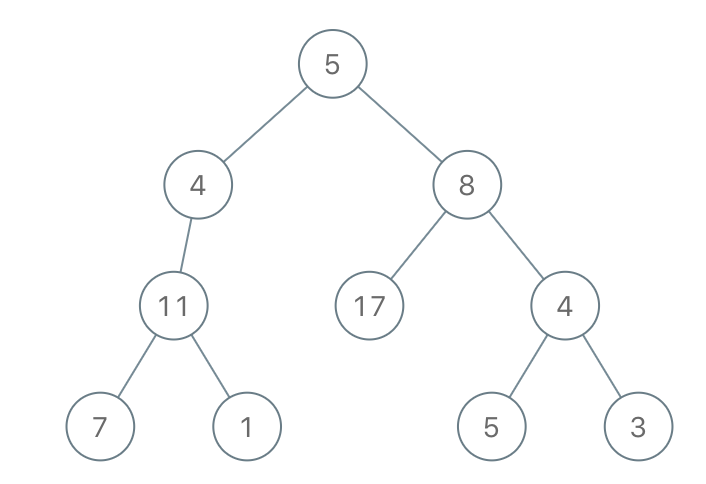
Input: root = [5,4,8,11,null,17,4,7,1,null,null,5,3], limit = 22 Output: [5,4,8,11,null,17,4,7,null,null,null,5]
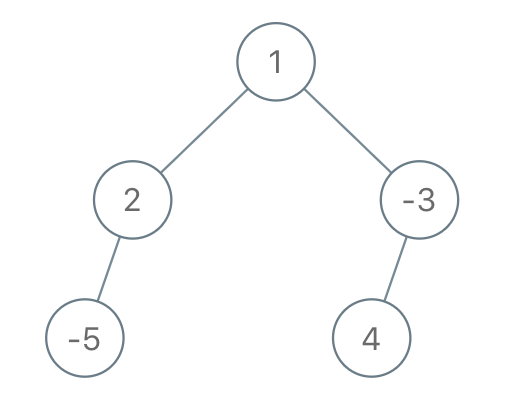
Input: root = [1,2,-3,-5,null,4,null], limit = -1 Output: [1,null,-3,4]
- The number of nodes in the tree is in the range
[1, 5000]. -105 <= Node.val <= 105-109 <= limit <= 109
# Definition for a binary tree node.# class TreeNode:# def __init__(self, val=0, left=None, right=None):# self.val = val# self.left = left# self.right = rightclassSolution: defsufficientSubset(self, root: Optional[TreeNode], limit: int) ->Optional[TreeNode]: defdfs(root: Optional[TreeNode]) ->None: ifrootisnotNone: ifroot.leftisnotNone: root.left.rootsum=root.rootsum+root.left.valifroot.rightisnotNone: root.right.rootsum=root.rootsum+root.right.valdfs(root.left) dfs(root.right) ifroot.leftisNoneandroot.rightisNone: root.leafsum=0elifroot.leftisNone: root.leafsum=root.right.leafsum+root.right.valelifroot.rightisNone: root.leafsum=root.left.leafsum+root.left.valelse: root.leafsum=max( root.left.leafsum+root.left.val, root.right.leafsum+root.right.val) root.rootsum=root.valdfs(root) ifroot.rootsum+root.leafsum<limit: returnNonenodes= [root] whilenodes!= []: node=nodes.pop() ifnode.leftisnotNone: ifnode.left.rootsum+node.left.leafsum<limit: node.left=Noneelse: nodes.append(node.left) ifnode.rightisnotNone: ifnode.right.rootsum+node.right.leafsum<limit: node.right=Noneelse: nodes.append(node.right) returnroot